The Evolution of GRC: From Check-the-Box to Strategic Asset
In a 2023 report by Thomson Reuters, an eye-opening statistic emerged: 70% of corporate risk and compliance professionals have observed a significant shift in their field. Over the past two to three years, there’s been a move away from the traditional ‘check-the-box’ compliance towards a more strategic and holistic approach.
This striking trend emphasizes the evolving nature of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC). It marks a paradigm shift in how companies perceive and integrate risk management and compliance into their core strategies. But what does the shift to a more strategic and holistic approach mean for the future of corporate governance and risk management, and how can businesses effectively adapt to this new landscape?

The Three Pillars of GRC
Understanding the three fundamental pillars of Governance, Risk, and Compliance is crucial for any organization seeking to navigate today’s business challenges with clarity and confidence. These pillars not only define the framework of GRC but also provide a roadmap for integrating it into every aspect of an organization’s operations.
Governance: Steering Towards Ethical and Strategic Excellence
At the heart of governance lies the commitment to direct and control an organization with a focus on integrity, ethical standards, and strategic alignment. Governance is the guiding force that ensures all business activities align with an organization’s objectives and values. This involves setting clear policies, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing accountability mechanisms.
In the context of cybersecurity, governance takes on a heightened significance. It involves crafting policies that protect data and systems, ensure privacy, and maintain stakeholder trust. This pillar is about creating rules and cultivating a culture where every team member understands their role in upholding the organization’s values and security protocols.
Risk Management: Navigating Uncertainties with Insight and Agility
Risk management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and addressing potential threats that could impact an organization’s goals. This dynamic and continuous process requires organizations to stay vigilant and responsive to internal and external changes.
In practice, risk management means recognizing financial or operational risks and understanding the complexities of cybersecurity threats. It’s about being proactive, not reactive, and making informed decisions that balance potential benefits against associated risks. Effective risk management enables an organization to safeguard its assets and seize opportunities in a way that aligns with its risk appetite.
Compliance: Upholding Standards and Building Trust
Compliance is the commitment to adhere to industry regulations, laws, and ethical standards. It’s an ongoing process of ensuring business practices align with external legal requirements and internal policies.
The value of compliance extends beyond simply avoiding legal penalties. It’s about building trust with customers, partners, and regulatory bodies. In cybersecurity, compliance means staying abreast of the latest data protection laws, industry standards, and best practices. It involves regular audits, training, and updating policies to reflect the latest regulatory changes.
Together, these three pillars form the foundation of GRC, providing a holistic approach to managing an organization’s governance, risk, and compliance. They are interdependent, each playing a critical role in the overall effectiveness of a GRC strategy. As we delve deeper into how these pillars are integrated into business strategy, we begin to see how GRC transcends its individual components to become a strategic asset, driving organizations toward sustainable success and resilience.
The Significance of GRC in Modern Business and Cybersecurity
GRC is not just a necessity but a strategic enabler. Its significance extends far beyond the traditional scope of meeting regulatory demands. GRC takes on a critical role in cybersecurity, addressing the challenges that arise when threats evolve rapidly and regulations struggle to keep pace.
Effective GRC implementation fosters a culture where risk management is ingrained in every decision, governance is transparent and effective, and compliance is seamlessly integrated into daily operations. This approach safeguards against potential threats and legal pitfalls and enhances overall organizational agility, credibility, and success.
Furthermore, GRC stands at the forefront of building resilience. In an era where uncertainties are prevalent, having a comprehensive GRC strategy equips organizations to navigate through disruptions, adapt to new challenges, and emerge stronger. By harmonizing governance, risk management, and compliance, businesses can forge a path that leads to sustained growth, enhanced security, and an unshakeable reputation in the eyes of stakeholders and customers alike.
As we venture deeper into the intricacies of GRC, it becomes evident that this triad is more than a set of practices. It’s a mindset, a strategic framework that enables businesses to thrive in a complex, interconnected world. Let’s uncover the layers of GRC and understand its profound impact on the modern business landscape.
The Strategic Role of GRC in Business
Integrating Governance, Risk, and Compliance within an organization’s strategy is not just about managing obligations; it’s about crafting a roadmap for sustainable growth and informed decision-making. This section explores how GRC aligns with business goals and transforms from a compliance necessity into a strategic business asset.
Alignment with Business Goals and Objectives
The essence of GRC lies in its ability to align seamlessly with an organization’s overarching goals and objectives. Governance frameworks guide the organization in setting and achieving its strategic objectives while maintaining ethical standards. Risk management processes ensure that these objectives are pursued with a clear understanding of the risks and mitigation strategies. Conversely, compliance guarantees that these objectives are met within the boundaries of legal and regulatory requirements.
This alignment goes beyond mere risk avoidance and regulatory adherence. It involves embedding GRC principles into the very fabric of organizational strategy, thereby enhancing decision-making processes. When GRC is interwoven with business goals, it enables leaders to make informed choices, foresee potential challenges, and capitalize on opportunities with a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Transformation of GRC from Compliance to Strategic Asset
GRC’s role in contemporary business has evolved significantly. Initially viewed as a set of constraints or a means to avoid penalties, it is now recognized as a strategic asset that can drive competitive advantage. This transformation is driven by the growing understanding that effective GRC practices protect and create value for the organization.
By integrating GRC into their strategy, businesses can achieve more than just compliance; they can unlock new efficiencies, improve risk resilience, and foster a culture of transparency and accountability. This, in turn, leads to enhanced stakeholder trust, a more motivated workforce, and a stronger market position.
For instance, a well-implemented GRC strategy can streamline processes, reduce redundancies, and lead to better resource allocation. It can provide insights that guide strategic planning and help businesses stay agile in the face of regulatory changes or market disruptions. A strategic approach to GRC can be the difference between a reactive stance and a proactive defense, enabling businesses to anticipate and mitigate cyber threats effectively.
The strategic integration of GRC into business practices marks a shift towards a more holistic, forward-thinking approach to governance, risk management, and compliance. This integration safeguards the organization and propels it towards achieving its long-term goals with confidence and clarity. As we turn our attention to the nuances of managed GRC services, we will explore how simplifying the complexity of these components can further enhance their strategic value.
Managed GRC Services: Simplifying Complexity
Embracing the full potential of Governance, Risk, and Compliance can be a challenging endeavor, especially in an environment where business complexities are constantly unfolding. Managed GRC services step in as a solution to simplify these complexities, offering a streamlined approach to integrating GRC practices into the core of business operations.
Concept of Managed GRC Services
Managed GRC services represent a strategic partnership where external expertise is brought in to enhance and oversee an organization’s GRC functions. This concept revolves around leveraging specialized knowledge and resources to manage the intricacies of governance, risk management, and compliance.
These services are designed not just to ensure that businesses meet their regulatory requirements but also to do so in a way that aligns with their specific goals and operational dynamics. They offer a tailored approach, recognizing each organization’s GRC needs are unique and require solutions that fit their context and challenges.
Supplementing Team Capabilities
The integration of managed GRC services into a business structure serves to supplement and empower internal teams. By bringing in specialized expertise, organizations can bridge gaps in their knowledge and capabilities, allowing internal resources to focus on core business activities.
These services work with existing teams, providing them with the tools and insights to make informed decisions. This collaboration can significantly reduce the strain on internal resources, especially in areas that require deep expertise, such as compliance with complex regulations or risk assessments in a rapidly changing cybersecurity landscape.
Managed GRC services can also bring a fresh perspective to existing practices, identifying areas for improvement and innovation. They can help streamline processes, eliminate redundancies, and implement best practices that enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
In summary, managed GRC services offer a way to navigate the multifaceted world of governance, risk, and compliance with greater ease and expertise. Organizations can turn GRC into a powerful tool for achieving strategic goals and maintaining operational resilience by aligning these services with business strategies and leveraging their potential to supplement internal capabilities. As we delve into the next section, we will explore how these services align business strategy with GRC standards, further enhancing the strategic value of GRC in the business context.

Aligning Business Strategy with GRC Standards
The harmonization of business strategy with Governance, Risk, and ComplianceGRC standards is a critical step towards ensuring that an organization’s objectives are achieved in a controlled and compliant manner. This alignment is fundamental to embedding GRC into the strategic fabric of the organization, turning it into a driver for informed decision-making and operational excellence.
The Process of Integrating Business Strategies with GRC Standards
Integrating business strategies with GRC standards begins with a thorough understanding of an organization’s objectives, the risks it faces, and the regulatory landscape in which it operates. This integration is a strategic process that involves several key steps:
- Assessment of Current Strategies and GRC Posture: This involves evaluating existing business strategies and understanding how GRC processes currently support these strategies. Identifying gaps where GRC processes may not fully align with business objectives is crucial.
- Identification of Regulatory and Risk Landscapes: Understanding the external environment, including regulatory requirements and potential risks that could impact business strategies, is essential. This helps in adapting strategies to be both compliant and resilient.
- Development of Aligned GRC Frameworks: Based on the assessment, developing or refining GRC frameworks that align with business strategies is key. This includes setting appropriate governance structures, risk management processes, and compliance protocols that support business objectives.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Once developed, these frameworks need to be implemented across the organization. Continuous monitoring and adjustment are necessary to ensure that the alignment remains relevant and effective in the face of changing business conditions and external environments.
Aligning business strategy with GRC standards is not just about compliance and risk management; it’s about strategically leveraging these aspects to support and enhance business objectives. This alignment is especially crucial in managing cybersecurity risks, where the proper GRC framework can provide a significant competitive advantage.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape with Precision
Navigating the regulatory landscape with precision is crucial for any business. This task, often complex and demanding, requires a nuanced understanding of various compliance requirements and the ability to apply them effectively within an organization’s operations.
Managed GRC services emerge as a vital ally in this context. They provide the expertise and tools necessary to navigate complex regulations effectively. Here’s how they make a difference:
- Expert Guidance: Managed GRC services bring specialized knowledge of various regulatory environments. They stay abreast of the latest changes, providing businesses with up-to-date advice.
- Customized Compliance Strategies: Understanding that each business is unique, these services help develop customized compliance strategies that align with specific business needs and regulatory requirements.
- Efficient Implementation: Leveraging their expertise, managed GRC services can streamline the implementation of compliance measures, ensuring they are integrated seamlessly into business processes without disrupting operations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Compliance is an ongoing process. Managed GRC services offer continuous monitoring and regular updates to compliance strategies, ensuring businesses remain aligned with current regulations.
Precisely navigating the regulatory landscape is not just about meeting the minimum requirements – it’s about strategically integrating compliance into the business fabric, ensuring it contributes to the organization’s overall efficiency, reputation, and success.
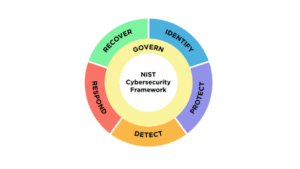
Specific GRC Services and Assessments
When it comes to GRC, tailored services and assessments are crucial tools for businesses striving to meet industry standards and regulations. Specific GRC services and assessments like NIST and CMMC are more than compliance exercises; they are integral to the strategic fortification of an organization’s cybersecurity and risk management posture.
NIST Assessments, conducted under the guidelines of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, offer businesses a comprehensive evaluation based on the NIST framework, which is recognized as a gold standard in cybersecurity practices. These assessments are instrumental in helping businesses gauge their current cybersecurity posture, pinpoint areas that need enhancement, and ensure their security strategies align with industry best practices. Adherence to NIST guidelines bolsters a company’s cybersecurity defenses and showcases its dedication to data security and effective risk management.
CMMC Assessments, centered around the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification, are crucial for companies engaging with the Department of Defense (DoD). This certification outlines a comprehensive set of cybersecurity standards and practices for safeguarding sensitive government data. Through CMMC assessments, a company’s readiness and adherence to these standards are meticulously evaluated, ensuring they achieve the necessary level of cybersecurity maturity. This process is vital for maintaining eligibility for DoD contracts. It plays a key role in protecting and securing sensitive government information.
Ensuring compliance and competitiveness through assessments goes beyond just meeting regulatory requirements; it is about maintaining a competitive edge in an industry where cybersecurity and adherence to compliance standards increasingly set businesses apart. These assessments provide insights that help businesses identify and address vulnerabilities, effectively mitigating risks to protect their operations and reputation.
Furthermore, demonstrating compliance with recognized standards like NIST and CMMC plays a significant role in bolstering stakeholder confidence by showing a dedication to high levels of security and governance. These assessments are not a one-off exercise but a part of an ongoing process of continuous improvement. They provide a structured framework that helps businesses remain agile and responsive in an environment characterized by rapid technological and regulatory changes.
Embracing GRC as a Strategic Asset
It’s clear that GRC is not merely a set of guidelines to be followed. Rather, it is a strategic asset that, when integrated effectively, can elevate an organization’s operational and strategic capabilities. It provides a framework for informed decision-making, ensuring that risks are understood and managed while compliance requirements are met. This framework empowers businesses to respond to immediate challenges and anticipate and prepare for future scenarios.
Businesses are urged to adopt a proactive approach to Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC), anticipating regulatory changes, understanding emerging risks, and weaving GRC principles into their core business strategies. Recognizing that GRC is a continuous journey of improvement and adaptation, especially as business and regulatory environments evolve, is crucial. Effective GRC implementation often requires partnerships and collaboration with experts, leveraging external resources to bring fresh perspectives and enhance the overall GRC framework.
Embracing GRC as a strategic asset is fundamental to achieving compliance and risk mitigation, operational excellence, and sustainable growth. As organizations navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world, the principles of GRC provide a solid foundation for resilience, innovation, and success.
60% of GRC users still manage compliance manually with spreadsheets. For organizations looking to eliminate inefficient GRC processes – and spreadsheets – Edge is here to be your guide. Our expertise in Governance, Risk, and Compliance can help transform these essential components into strategic assets for your business. Contact us for more information or to schedule a consultation, and take the first step towards integrating GRC into your strategic framework.