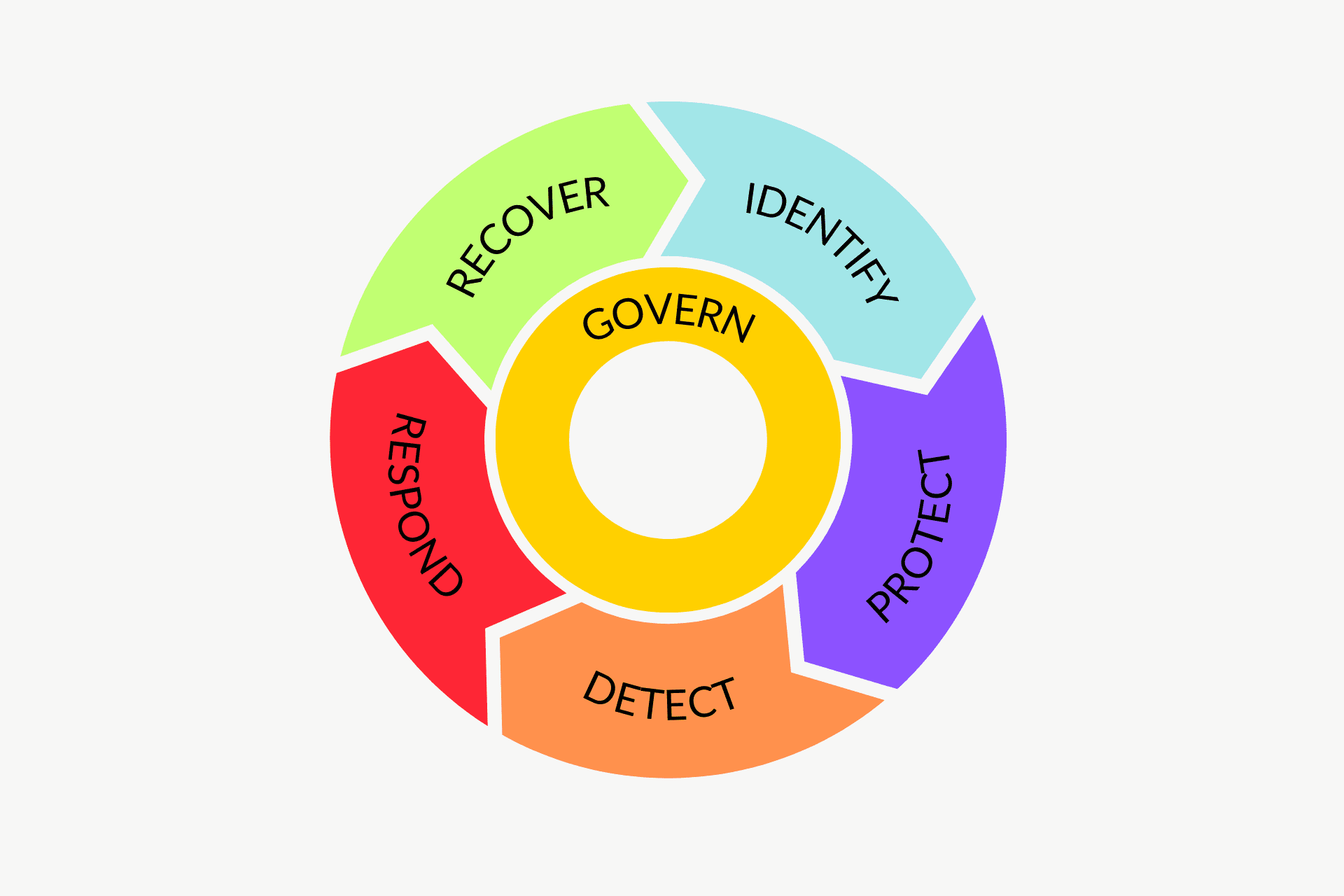
Join us as we dive into Microsoft Secure Score and how it can help you strengthen your organization’s security posture.
We’ll cover how to easily track your score, implement simple yet impactful security improvements, and integrate Secure Score with powerful tools like Microsoft Defender, Compliance Center, and Azure AD to create a robust security framework.
Whether you’re looking to boost endpoint protection, enhance identity security, or ensure compliance, this session will give you practical insights and actionable steps to protect your organization.
Watched this webinar and still need some help or don’t want to do it yourself? We got you.