This article was originally published September 2021. Updated April 2024.
What is Data Loss Prevention (DLP)?
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a broad term for a set of software, procedures, and other tools used to protect sensitive data. DLP software is used to identify confidential data and ensure that it’s properly encrypted and transmitted. “Confidential data” can vary depending on your business. It can include sensitive customer financial data, personal information covered by GDPR, or health information covered by HIPAA, among others. This data must be protected not just in storage but also when it’s being transferred or used. Because of the broad scope of this kind of data, DLP software usually relies on multiple components, or a complete suite, to detect breaches. Attempted breaches, or suspected attempts, can be escalated to human personnel for further review.
A basic example of DLP in action is the password policy for your mobile banking app. Passwords are required to have a certain number of characters, typically at least eight. They’re also usually required to contain some combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. If you try to create a shorter password or one without the required combination of characters, the app won’t let you. From the developer’s perspective, it’s automatically redirecting user behavior to ensure compliance with security best practices.
Of course, DLP in the real world is often more complex than simple password requirements. If you’re handling valuable customer information, trade secrets, or other sensitive data, you’re potentially exposed to infiltration from organized criminals, foreign governments, and even corporate rivals from countries that don’t mind corporate espionage. You’re also exposed to risk from human error, like the Royal Navy officer who left his laptop on a train, along with personal data on over 600,000 British sailors.
The potential costs are not trivial. The 2017 Equifax data breach cost the company almost $2 billion , an expense that would send most companies into bankruptcy. A 2013 breach of Yahoo’s systems exposed the personal information associated with more than 3 billion accounts . We’re about to discuss how data loss prevention helps prevent this kind of disaster.
Data Loss Prevention Basics
How Does Data Get Lost?
So, how does data loss happen? There are several common causes, but here are the three most common:
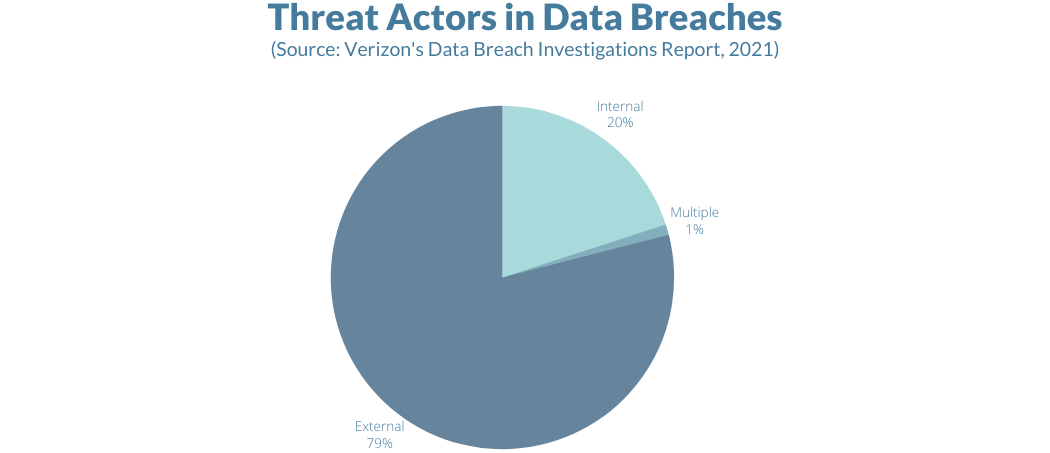
Insider attacks
Outside attacks
Attackers may use phishing and other techniques to install malware on network computers. Once inside, the malware looks for sensitive data and transmits it back to the attackers. Learn more about phishing by reading the post below.
Accidental leaks/human error
Essential Components of Data Loss Prevention
1. Securing data in storage
2. Securing data in transit
Monitoring secure data as it travels through the network to ensure it’s only accessible to approved users.
3. Securing data in use
4. Securing network connections
5. Data identification
6. Data monitoring
10 Ways Data Loss Prevention Benefits Your Company
So, how does data loss prevention benefit your company? Here are ten ways.
1. You Gain Real-Time Visibility Into Your Data
2. Your Organization Needs a Plan For Internal Threats
3. Breaches Cost More the Longer They Go Undetected
4. DLP Helps You Stay Compliant
5. DLP Reduces Your Exposure From Third-Party Devices
6. You Can Monitor Your Employees
7. You’ll Be Protected from Cloud-Based Threats
8. You Can Monitor Your Endpoints
The main risk for any network is at its endpoints – anywhere data is transferred between the company network and the broader web. Inside your network, you control your data. Once that data leaves the network, it’s “in the wild,” and you can no longer control what happens with it. DLP software monitors your endpoints, including physical endpoints like workstations and virtual endpoints like outgoing and incoming email. This stops many forms of harmful activity before they even start.
9. You’ll Spend Less on IT
10. Your Customers Will Trust You More
Get Started on Your Data Loss Prevention Journey
Backup and disaster recovery is just one of the services we offer at Edge Networks. If you’re interested in learning more, contact us today . We take the time to understand your unique business needs and customize solutions to meet them, and we deliver technologies that boost productivity, performance, and business growth